Understanding the Heart’s Electrical System
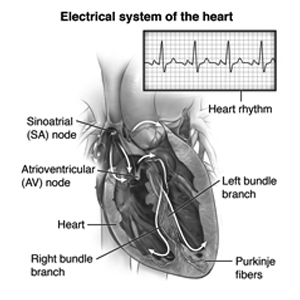
The heart functions on a muscular pump that is controlled and transmitted by electric signals via specific pathways. It starts with the specific sinus node, also called the SA node, in the right atrium. It generates an electric impulse that ranges from 60 to 100 times per minute to start each heartbeat. These impulses start through the atria to the atrioventricular, which is called the AV node. It’s located at the end of the right atrium. From here, they go along with the Bundle of His, an electric conduction pathway, and then through the His-Purkinje system, causing the ventricles to contract. This contraction transports blood throughout the body, ensuring circulation.
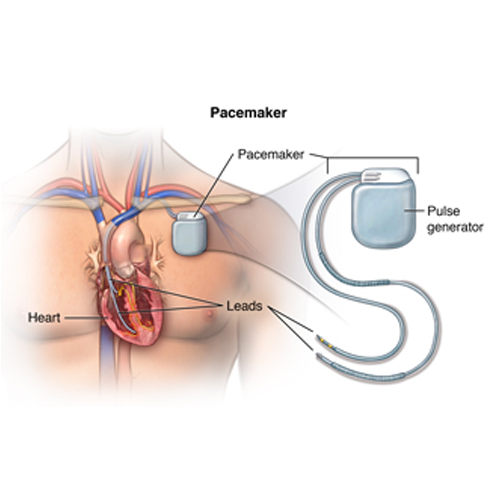
When this electrical conduction system fails then it causes weak heartbeats or signal transmission difficulties, you will need a pacemaker. A pacemaker regulates your heart’s rhythm by generating electrical pulses that maintain proper contraction timing and blood circulation.
Now Understand Why Pacemaker Insertion Is Necessary.
- Pacemaker insertion can help with slow or irregular heartbeats.
- It prevents fatigue, dizziness, and fainting.
- Keeps the heart at the proper rate, which increases blood flow.
- Reduces the risks associated with a shortage of blood flow in the body.
- It facilitates normal daily activities while lowering the need for medical interventions.
Let’s understand Pacemaker Insertion
Patients with abnormal heart rhythms require pacemaker placement. A tiny electrical device is thrust into the skin right below the collarbone. And this piece of equipment, known as a pacemaker, monitors cardiac electrical activity and sends electrical impulses to regulate the pulse as needed. Its primary application is to treat conditions in which the heart beats excessively slowly (bradycardia) or too frequently (arrhythmias).
When evaluating heart health and function, a variety of diagnostic methods are used to provide thorough insights into cardiac problems. These procedures range from non-invasive diagnostics to more invasive ones, with each serving a specific purpose in the diagnosis and monitoring of cardiovascular health.
Purpose: Purpose: It is a tool for measuring the electrical activity of the heart at rest and during exercise in order to detect anomalies such as arrhythmias or ischemia.
Purpose: A portable device placed by the patient that constantly records heart rhythms over time (typically 24-48 hours) in order to detect intermittent cardiac problems.
Purpose: Improves the detection of tiny electrical impulses in the heart, which can help identify potential arrhythmia concerns.
Purpose: An invasive technique in which a narrow tube (catheter) is introduced into a blood vessel and guided to the heart to diagnose and treat a variety of heart ailments, including coronary artery disease.
Purpose: Creates an image of the heart, lungs, and surrounding structures to help determine heart size, shape, and the presence of fluid or abnormalities.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest:
Purpose: X-rays are used to provide comprehensive cross-sectional images of the heart and blood vessels, which are useful for diagnosing coronary artery disease and other cardiac disorders.
Purpose: The instrument uses ultrasound to generate moving images of the heart’s structure and function, including its valves and pumping capabilities.
- Electrophysiology Studies:
Purpose: An invasive technique that examines the heart’s electrical circuitry and can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias and other electrical issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Heart:
Purpose: Uses massive magnets and radio waves to provide comprehensive images of the heart’s structure and function. Patients with pacemakers should see their cardiologist about potential interference from the MRI’s magnetic fields.
- Myocardial Perfusion Scan (Stress and Resting):
Purpose: Nuclear medicine studies that measure blood flow to the heart muscle can detect locations with insufficient blood supply, which may suggest coronary artery disease.
- Radionuclide Angiography:
Purpose: Radioactive tracers are used to generate images of blood flow through heart chambers and blood vessels, which aids in the diagnosis of heart problems.
Purpose: Provides detailed 3D images of the heart and blood vessels, which are important for diagnosing and assessing coronary artery disease and other cardiac diseases.
Each of these procedures is essential for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating a variety of cardiac diseases. The appropriate test is determined by the individual clinical circumstances, the patient’s symptoms, and the information required to provide an accurate diagnosis. Patient safety and comfort are priority, with careful attention given to the risks and advantages of each surgery, especially for those with unique needs such as pacemakers. Consultation with a Cardiac Specialist Doctor in Indore ensures that these diagnostic tests are selected and performed correctly to optimize cardiac care.
Reasons for the procedure
A pacemaker is a small device inserted into the chest to help manage certain heart problems. Here’s why your Best Cardiologist Clinic in Indore might recommend one:
- Slow Heart Rate (Bradycardia): When the heart beats too slowly, a pacemaker can transmit electrical signals to stimulate a quicker beating, ensuring that the body receives adequate blood and oxygen.
- Irregular Heart Rhythm (Tachy-Brady Syndrome): This syndrome produces alternating fast and slow heartbeats. A pacemaker can regulate the heart rate, preventing abnormally fast or sluggish beats.
- Heart block: Heart block occurs when the heart’s electrical signals are delayed or inhibited. A pacemaker can treat many forms of heart blockage and keep the heart beating regularly.
When the heart fails to pump blood properly, symptoms such as weariness, dizziness, fainting, or chest pain might develop. Your doctor may suggest a pacemaker to help regulate your heart rate and improve overall heart function. There could be additional reasons, so talk to your Best Heart Health Center in Indore about why a pacemaker is best for you and ask them about their pacemaker services in Indore.
Risks of the procedure:-
Here are the risks associated with pacemaker insertion, summarized point-by-point:
- Bleeding: Possible from the incision or catheter insertion site.
- Damage to Blood Vessels: Risk of injury to vessels where the catheter is inserted.
- Infection: Potential for infection at the site of the incision or catheter.
- Pneumothorax: An accidental puncture of the lung during the procedure can lead to air leaking into the chest cavity, causing breathing difficulties or a collapsed lung.
- Special Considerations for Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Notify healthcare providers if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Allergic Reactions: Patients allergic to medications or sensitive to latex should inform their doctor.
- Discomfort: Some patients may experience discomfort from having to lie still during the procedure.
- Other Risks: Depending on individual medical conditions, there may be additional risks specific to the patient.
Before a pacemaker procedure, follow these steps:
- Sign a consent form after understanding the procedure.
- Notify your doctor of allergies and sensitivities.
- Fast overnight, as instructed.
- Inform them about pregnancy or medications.
- Blood tests may be required.
- You may receive a sedative; plan for someone to drive you home.
- Expect to spend at least one night in the hospital for observation.
During a pacemaker insertion:
- Remove the jewellery and change into a gown.
- Empty your bladder beforehand.
- An IV line will be started for medications and fluids.
- Lie on your back on the procedure table.
- Electrodes monitor your heart’s activity.
- Sedatives are given through IVs to relax you.
- The insertion site is cleaned and numbed.
- A small incision is made, and a sheath is inserted into a blood vessel.
- Lead wires are guided through the sheath into your heart.
- The pacemaker generator is placed under the skin near your collarbone.
- The incision is closed, and a sterile dressing is applied.
After Pacemaker Insertion:
In the Hospital:
- Monitor vital signs and notify nurses of any chest pain or incision discomfort.
- Start moving slowly once bed rest ends; nurses will assist and monitor blood pressure changes.
- Eat and drink once fully awake; pain medication may be provided.
- The Pacemaker Surgery Doctors in Indore will give instructions and answer questions; stay until stable for discharge.
- Expect to spend at least one night in the hospital for observation.
At Home:
- Resume daily activities gradually; avoid heavy lifting.
- Follow a normal diet unless advised otherwise.
- Keep the insertion site dry and clean, as directed.
- Receive guidance on driving and returning to work.
- Contact a Pacemaker Implantation Hospital in Indore for concerns like fever, increased pain, or unusual symptoms.
- Follow specific instructions from your doctor based on your recovery progress.
Pacemaker Precautions:
- Carry an ID card and wear a medical bracelet indicating you have a pacemaker.
- Notify airport security about your pacemaker; minimize exposure to magnetic fields.
- Avoid MRI procedures and high-voltage machinery.
- Inform surgeons about your pacemaker before any procedure.
- Protect the pacemaker from physical impact during activities.
- Avoid smartphones at least 6 inches from your pacemaker.
- Consult your doctor for any concerns or new activities.
Consult Today for More Details.
For expert guidance in pacemaker surgery, contact us at The Heart Care Clinic. Our skilled doctors specialize in pacemaker implantation, ensuring safe and effective procedures. We provide advanced care in a state-of-the-art facility dedicated to your cardiac health. Trust our experienced team for comprehensive Pacemaker Services in Indore. Contact us today to schedule a consultation or learn more about our Pacemaker Implantation Hospital in Indore